The power of interest-only interest compound interest
The Concept of Interest
Interest is a kind of fee paid by a borrower to their lender for the funds lent. Interest should be thought of as the rent of money. It can be observed that the person who pays the interest is always considered high and the person who receives it is always low. Anyone who forgoes their money and thereby forgoes the material goods available for their money for a while and takes the risk that they may not even get their money back is entitled to expect to receive interest for this sacrifice. Therefore, the money has a time value, a few hundred dollars is worth more today than it will possibly be tomorrow or even a month from now.

Concept and Calculation Of Interest-only Interest
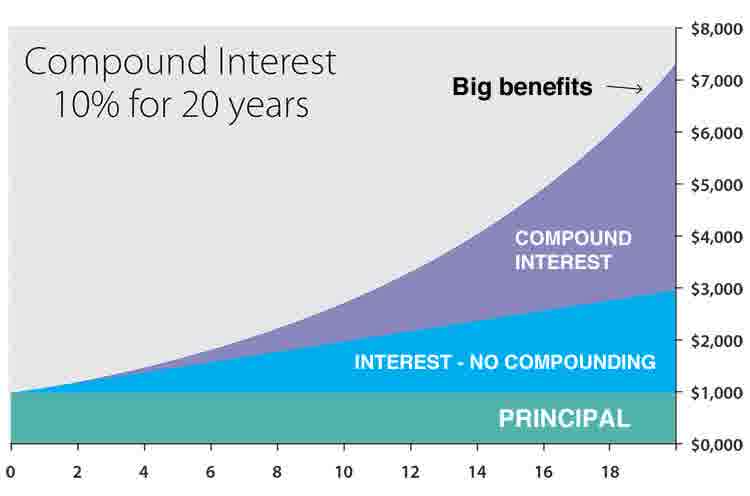
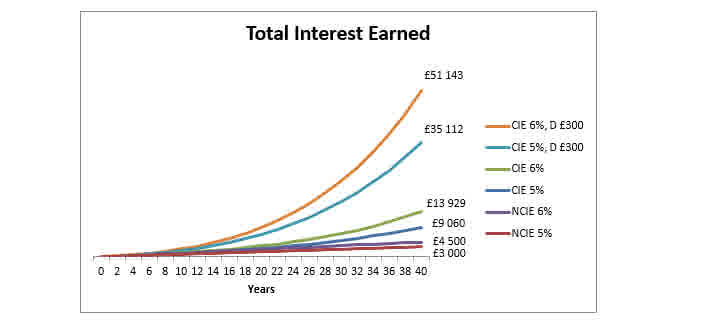
Compound interest is generated when collective interest is added to the loaned money. This is because, from this moment on, in addition to the loan itself, the added interest will go towards accruing more resulting interest than in the initial period. For example, suppose the bank pays 10% interest per year. If we put $10,000 into the bank, it will bring interest of an extra $1000 by the end of the first year. If we then leave the initial amount plus that interest in the bank, by the end of the second year it will bring in more interest than the first year – This would now be $1,100 of interest earned.
Exactly how do we work out our earned interest for each year?
We take the initial investment and multiply it $10,000 * $0.1 = $1,100. Following this formula, we can see that by the end of the second year, there would now be a total of $12,210 in the account.
Learn more about compound interest here is a link to wikipedia

Interest Rate Calculator
Attention! In the world of the stock market, monthly yields (interest) are more often calculated.
There are several reasons for this:
1. On an annual basis, the yield available on the stock market would be too high and thus figures that would be completely incomprehensible to people less familiar with the stock market would come out.
2. Since there are strategies where it is worth taking part of the earnings (profit) regularly (every 2-3 months), it is easier to calculate monthly percentages.
Please note: If you want to use decimal numbers, enter a decimal point, not a decimal point.
For the Initial Amount, enter the amount you want to invest.
For Monthly Interest, enter the percentage of return you want per month.
For Months, enter how many months you want your money to be used for.
When you click on another field, the calculator always calculates the last two fields:
The Total is replaced by the amount by which the money multiplies.
The total return (profit) is replaced by the profit on the initial amount invested.
Try the following values:
1.
Initial amount: 10.000
Monthly interest %: 15
Number of months: 72
2.
Initial amount: 100.000
Monthly interest %: 5
Number of months: 96
3.
Initial amount: 1.000.000
Monthly interest %: 10
Number of months: 120
Investment Compounding Calculator
Read more from Us